Authors
Woojin Jung1, Koung Mi Kang2, Hongjun An3, Seoung Hong Choi2
2Seoul National University Hospital, Korea, Republic of
3Seoul National University, Korea, Republic of
[email protected]
KCR (2023)
PURPOSE
MR-based brain volumetry software have been developed for clinical use. However, each software provides normative percentile (NP) based on data from different populations, without considering the potential differences in volumetric distributions across races. We constructed Asian and Non-Asian normative databases and calculated NP from each database using a novel deep learning-based volumetric algorithm (DL model). Then, we compared hippocampal volumetric results between the DL model and two volumetry software to demonstrate the racial differences.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
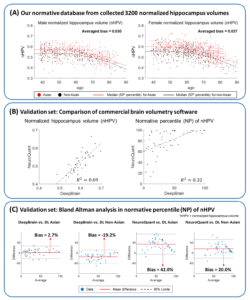
This retrospective study was approved by IRB. 3200 3D T1-weighted scans were collected from subjects without structural brain abnormalities aged 35 to 90 years. All scans were collected from the institution and a public database, resulting 1600/1600 scans for Asian/Non-Asian normative database. We developed a DL model using 1336 scans with Freesurfer-based manual segmentation labeling. Using the DL model, the normalized hippocampus volume (nHPV= HPV/intracranial volume) of each subject was estimated, generating Asian/Non-Asian nHPV normative databases. To validate our normative databases, a validation set was acquired from 48 Asians using 3D MPRAGE in 3T with TR/TE/TI = 1740/2.8/900 ms, voxel size = 1 x 1 x 1 mm3. In the validation set, nHPV and its NP were compared between two volumetry software: DeepBrain (Vuno, known for Asian normative database) and NeuroQuant (Cortechs.ai, known for Non-Asian normative database). In addition, we calculated NP values of nHPV using our DL model with Asian normative database (DL Asian) and with Non-Asian normative database (DL Non-Asian), and compared them with DeepBrain and NeuroQuant by Bland-Altman analysis.
RESULTS
Our nHPV normative database showed a bias in NP between Asian and Non-Asian (male/female = 0.030/0.037), revealing the racial difference (Fig A). Validation set results (Fig B) showed a high correlation between nHPV of DeepBrain and NeuroQuant (R2=0.69), but a low correlation for NP (R2=0.32). Bland-Altman plots showed the bias range (mean ± SD) as (2.7 ± 15.3) in DeepBrain vs. DL Asian, (-19.2 ± 16.9) in DeepBrain vs. DL Non-Asian, (42.0 ± 25.1) in NeuroQuant vs. DL Asian, and (20.0 ± 23.2) in NeuroQuant vs. DL Non-Asian (Fig C), suggesting low correlation of NP between the two software (Fig B) may originate from different NP distributions across races.
CONCLUSION
Normative databases based on different racial groups significantly affect the accuracy of NPs in brain volumetry.

